Blepharitis
What is blepharitis?
Blepharitis is a common inflammation of the eyelids’ margins and the glands within them, causing redness, irritation, and itchiness. It is a long-term condition that can be controlled with treatment but it is known to have intermittent flare ups. It is not sight-threatening or contagious.
Blepharitis is caused by the blockage and inflammation of small glands (Meibomian glands) on the eyelid margins which normally produce the oily component of the tear film that protects and lubricates the eye. There are around 30 of these small glands on each eyelid, and are located behind the lashes. Blockage and inflammation of these glands causes tears to evaporate quickly and the patient develops symptoms of dry, gritty eyes.
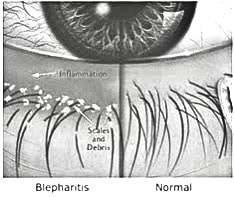
The eyelids may appear swollen with crusty or flaky skin around the edges. They might be sticky when waking up in the morning. The eyes might be predominantly dry, or even watery as the tear (lacrimal) glands are trying to compensate for the unstable tear film. The eyes sometimes become sore, red and irritated. Uncontrolled cases might lead to recurrent chalazions, loss of lashes, lashes turning inwards or corneal ulceration and scarring.
Treatment
There is no cure for blepharitis, but the flare ups and symptoms can be improved.
The following advice can help to control the symptoms and needs to be applied for prolonged periods of time, sometimes life-long:
- Hot compresses/ Heatable masks
- Lubrication drops/artificial tears as needed
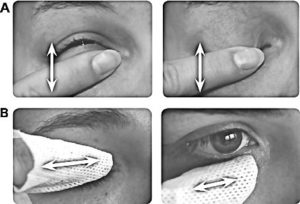
- Gentle lid massage, as shown below
- Omega-3 oral supplements
- Short course of topical anti-inflammatory drops, or antibiotics by mouth might be indicated in some cases
Further tips:
- Thoroughly clean eyes after eye makeup use and consider changing eye make-up
- Allow a few weeks of treatment before noticing improvement
Other considerations
Blepharitis can be associated with some skin conditions such as:
- Rosacea, which causes the face to appear red and blotchy. Mainstay for treatment of ocular rosacea is specific oral antibiotics.
- Seborrhoeic dermatitis, which causes an itchy rash on the skin and scalp (seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp is called dandruff)
- Acne in teenager and young adults, which cases irritation and blockage of the glands in the centre of the face
- Blepharitis can be a side effect of medications such as retinoids and chemotherapy drugs.
Useful links
NHS – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/blepharitis/
RNIB – https://www.rcophth.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/2017_Understanding-Dry-eye.pdf
American Academy of Ophthalmology – https://www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/what-is-blepharitis
Health & care video library – https://healthandcarevideos.uk/eyes?videoId=4426
