Blood clots, reducing the risks – easy read version
Information about what to do to stop getting a blood clot and keep you healthy when you have a stay in hospital and when you go home.
What are blood clots?
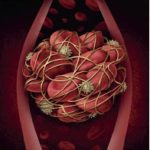 A blood clot is a hard lump of blood that can form inside your body.
A blood clot is a hard lump of blood that can form inside your body.
Sometimes it can make you very ill.
Who can get a blood clot?
Anyone can get a blood clot. You are more at risk if you are pregnant, ill or having an operation in hospital
What can you do to help?
Stay active 
Drink plenty
Do exercises to improve your blood flow 
Blood flow exercises
Always check with your doctor if you can do these exercises. They help keep you healthy.
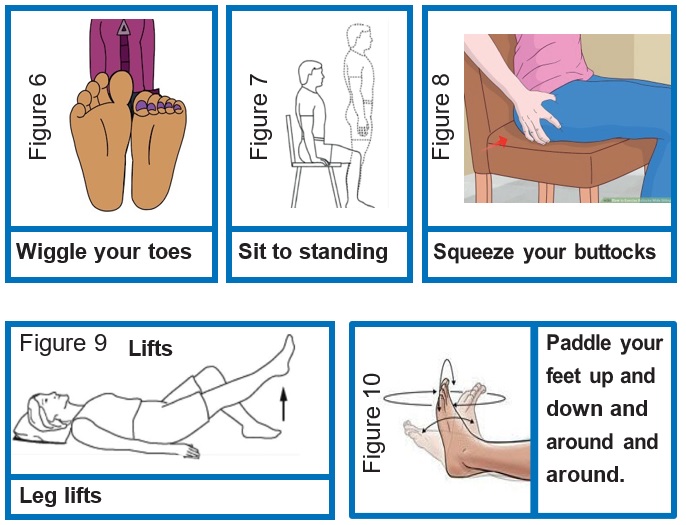
Do 10 repetitions of each exercise at least 3 times a day
Exercise for the legs – you can do it!
Breathing exercises – try them!

What will the hospital do to help?
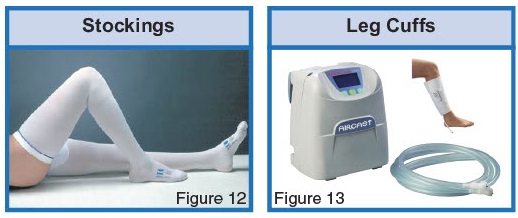
The doctor may give you stockings and / or leg cuffs to help the blood flow better in your legs.
The doctor may give you a medicine (injection or tablets)
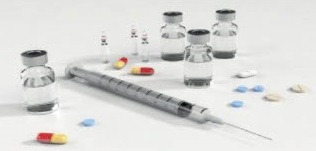
Are these treatments safe?
Stockings and leg cuffs

Sometimes stockings and leg cuffs can make the skin on your legs go red or break. This can happen if they are too tight and dig in to your skin. If it happens let your doctor know straight away.
Medicines (injection or tablets)

These medicines protect you from blood clots but sometimes they can give you:
- Allergy (like a rash)
- Bruises
- Bleeding (e.g. nosebleeds, heavy periods, internal bleeding)
How do you know if you have a blood clot?
If you feel:
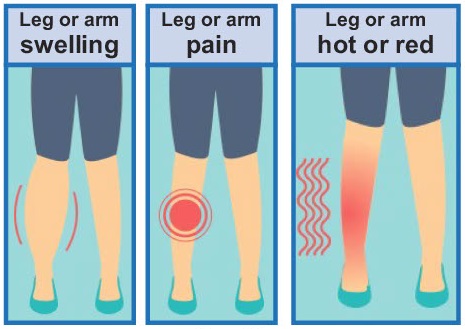
You may have a blood clot.
Tell your nurse or doctor straight away
How do you know if you have a blood clot?
If you feel:
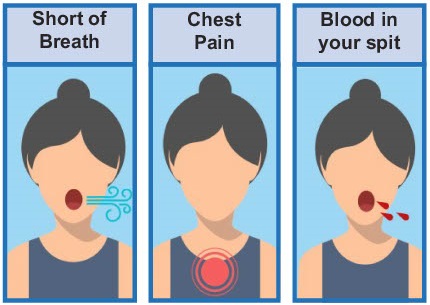
You may have a blood clot.
Tell your nurse or doctor straight away.
Advice for when you go home
You can still get a blood clot after going home, especially in the first 3 months. Make sure that you…
Stay active
Drink plenty
Do exercises to improve your blood flow 
The doctor may ask you to wear stockings and continue the medicines at home for a while. Make sure that you…
Wear the stockings, take the medication.
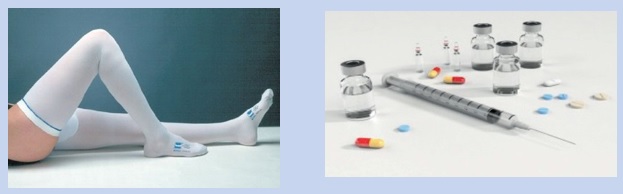
Further useful information
- Trust Patient Medicines Helpline: 01296 31 6197
- Venous thromboembolism in over 16s: reducing the risk of hospital-acquired deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism
- NHS information about blood clots
- Download the Preventing VTE App
